PLATFORM TECHNOLOGY
ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION
PLATFORM TECHNOLOGY
ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION
ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION
Vascular endothelial dysfunction is an early pathogenesis factor in cardiovascular disease, consisting of impaired vasodilation, angiogenesis, and barrier dysfunction. Vascular endothelial dysfunction is associated with metabolic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, which are linked to cardiovascular disease. Oxidative stress and inflammation play a major role in the pathogenesis of blood and endothelial dysfunction.
Endothelial dysfunction in aging & vascular associated diseases


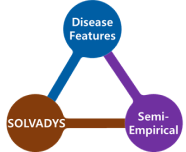
Curacle’s SOLVADYS® Strategy

CURACLE’S Approach
“SPAR: Phenotype-Based Approach & Structure-Phenotypic Activity Relationship”
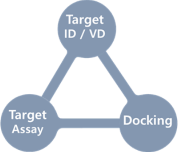
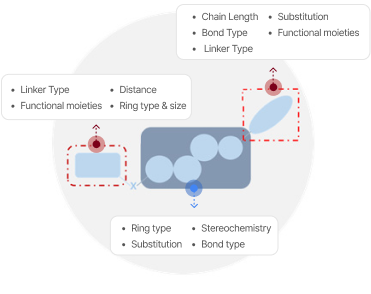
Establishment of SPAR

CU06 Development as the first endothelial dysfunction blocker
Sequential
phenotype-based
screening


