Pipeline
CU104
Pipeline
CU104
CU104
Expanded indication of CU06 for Ulcerative Colitis
| Sortation | content |
|---|---|
| CU104 | Expanded indication of CU06 for Ulcerative Colitis |
| Indication |
Ulcerative Colitis
• Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease with unknown etiology characterized by inflammation localized in the mucosa or submucosal layer of the large intestine. • The exact cause of the disease is not yet known, but environmental factors, genetic factors, and excessive immune responses are considered the main causes of the disease. • Common symptoms are bloody or mucosal stool and diarrhea, and chronic bleeding may lead to anemia. • Mesalazine, a drug mainly used to treat ulcerative colitis, is an anti-inflammatory drug that can cause various side effects (nausea, heartburn, headaches, dizziness, anemia, rash, etc.), so there is an urgent need to develop safe drugs that can improve patients’ quality of life. |
| Unmet Needs |
• The TNF-α inhibitors are the mainstay of biological treatment for moderate to severe UC. However, these agents carry safety risks and have efficacy limitations. • CAM inhibitors (Vedolizumab), oral Jak inhibitors (Tofacitinib), and IL-12/23 inhibitors (Ustekinumab) have expanded the treatment options for moderate to severe UC, but despite the number of currently available agents, a significant unmet need exists, especially for patients refractory to these therapies. |
| Mechanism of Action |
• Mediates endothelial cell homeostasis; Inhibits vascular abnormalities and inflammation induced by various vascular endothelial activators. • Reduces abnormal vessels and the destruction of the vascular barrier by inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 levels. • Strengthens endothelial cell junctions by upregulating the expression of junction proteins (Occludin, ZO-1, Claudin 5). |
| Efficacy & Safety |
• CU104 showed a greater improvement in histological features, leukocyte infiltration, and vascular normalization. |
| Market |
• 7.1 billion US$ in 2021 (8 Major Markets*) *US, EU5, Japan, Canada • Forecasted to be 11.2 billion US$ by 2029 (8 Major Markets) |
Indication
Cause
Incidence, Mortality
Symptoms
Unmet Needs
Mechanism of Action
Efficacy
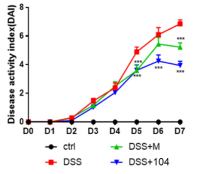
Attenuation of clinical features

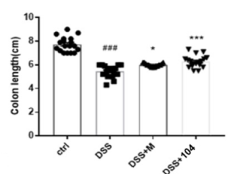

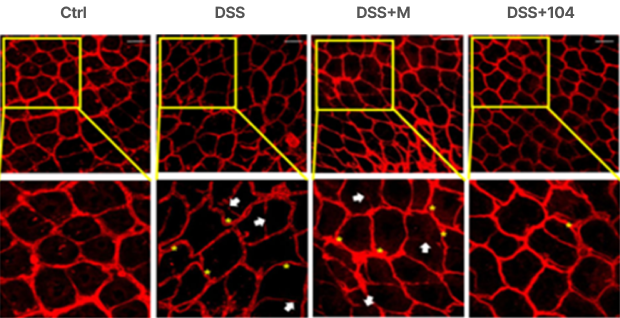
Prevention of tissue damage and the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the colon
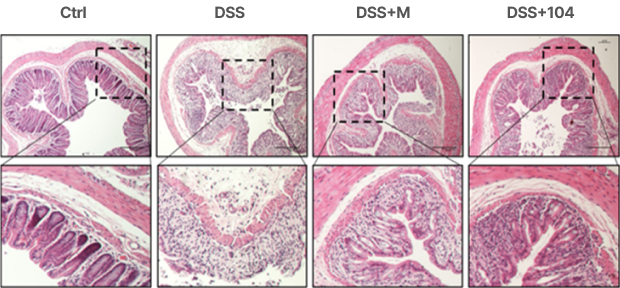
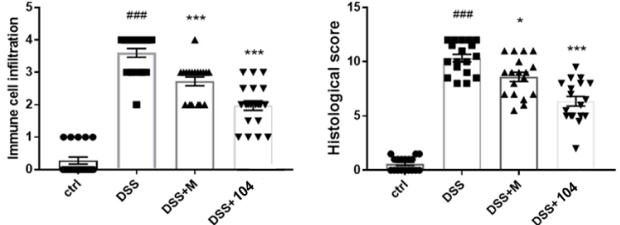
Stabilization of blood vessel integrity in the colon: Increased diameter of colorectal blood vessels
Superior efficacy compared to Mesalazine

Safety
CU104 has multiple actions to block vascular leakage and inflammation while maintaining the survival and stability of vascular endothelial cells and no toxicity was observed in nonclinical studies.