Pipeline
CU106
Pipeline
CU106
CU106
Expanded indication of CU06 for Immuno-Oncology Combination Therapy
| Sortation | content |
|---|---|
| CU106 | Expanded indication of CU06 for Immuno-Oncology Combination Therapy |
| Indication | Immuno-Oncology Combination Therapy |
| Unmet Needs |
• Immune checkpoint inhibitors have been shown to be only effective against certain types of cancer such as melanoma, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and liver cancer. • Immuno-suppression created by the abnormal TME (tumor microenvironment) vasculature cannot be modified by anti-PD-1 therapy. • Vascular stabilization may increase the efficacy of immunotherapy by normalizing blood vessel perfusion. |
| Mechanism of Action |
• Improves anti-PD1 delivery through normalized tumor vessels and promotes tumor apoptosis. • Reduces hypoxia and increases CD8+ T-cell infiltration that kills tumor cells within the central region of the tumor. • Improves tumor vascular normalization and decreases uncontrolled tumor angiogenesis. |
| Efficacy & Safety |
• Improvement in tumor vascular normalization and hypoxia • Enhancing the function of tumor infiltration CD8+ T cells decreases uncontrolled tumor angiogenesis |
| Market |
• By 2025, Immuno-Oncology drugs are expected to account for $56 billion, or 25% of the total oncology drug market. |
Indication
Cause
Unmet Needs
Mechanism of Action
![]()
![]()
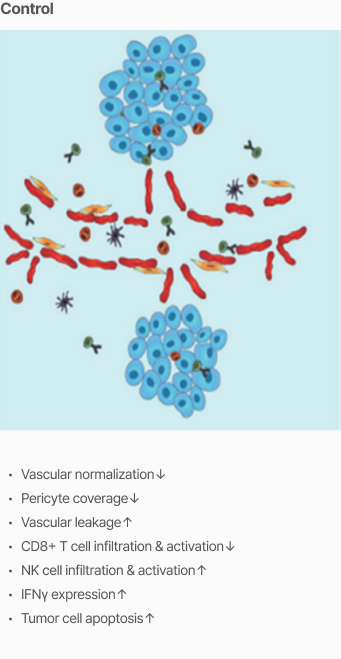
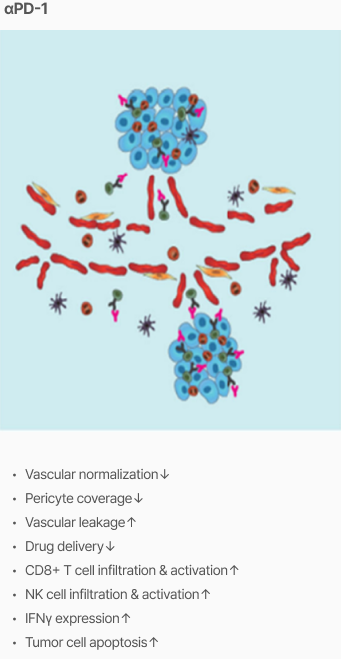
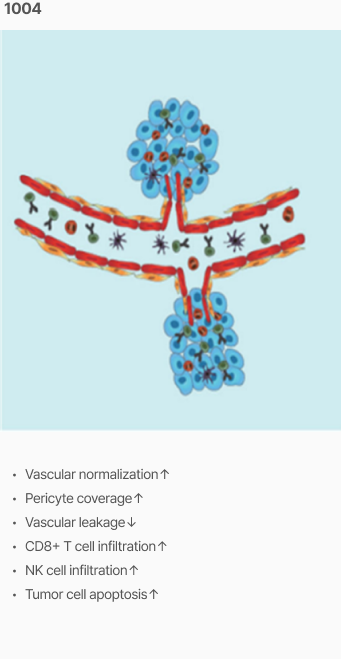
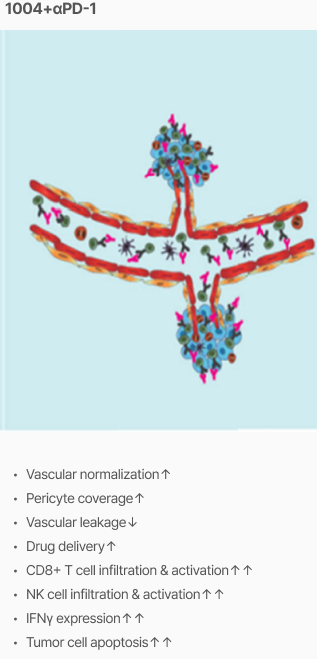
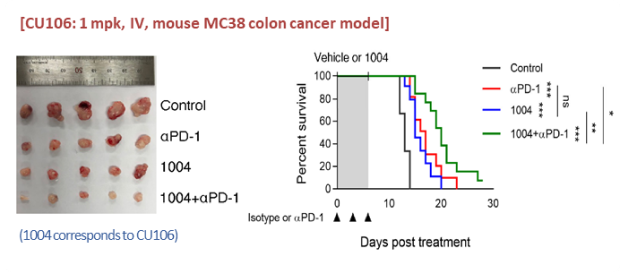
Efficacy
Inhibition of tumor growth and extension of survival
‘CU106 + αPD-1’ inhibits tumor growth (colon cancer) and extends mouse survival
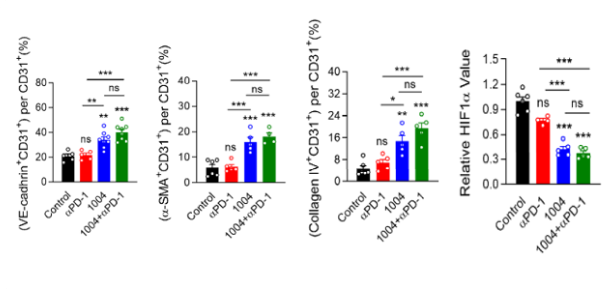
Tumor vascular normalization
‘CU106 + αPD-1’ improved tumor vascular normalization and decreased hypoxia & abnormal vessel density
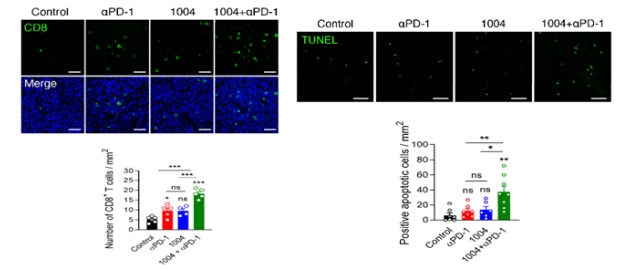
Promotion of CD8+ T cells and apoptosis
‘CU106 + αPD-1’ promotes accumulation of CD8+ T cells and apoptosis in tumors
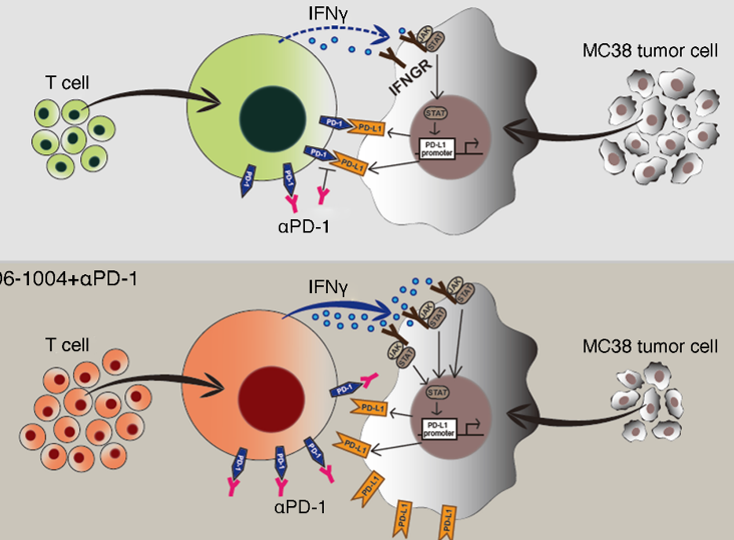
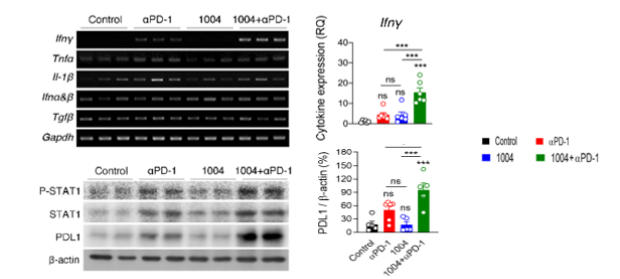
Improvement of tumor specific CT8+ T cell response
‘CU106 + αPD-1’ improves tumor specific CD8+ T cell response in spleen and tumor tissue (secretion of IFNγ -> upregulation of PD-L1 expression by regulating STAT1)
Development
Ongoing Study : IL-2 agonist and CU106 combination mouse model