Pipeline
CU105
Pipeline
CU105
CU105
Expanded indications of CU06 to Hereditary Angioedema(HAE)
| Sortation | content |
|---|---|
| CU105 | Expanded indications of CU06 to Hereditary Angioedema(HAE) |
| Indication | Hereditary Angioedema(HAE) |
| Unmet Needs |
• Approved HAE treatments can minimize the risk of death, but they are not effective in complete healing from the disease. • The new gene therapies seem to provide promising opportunities for the treatment of hereditary angioedema.
• However, there are still many unmet needs, including efficacy, route, and timing of administration
|
| Mechanism of Action |
• Treatment of HAE through normalization of endothelial cell barrier |
| Efficacy & Safety |
• Prevention of vascular hyperpermeability. • Inhibition of BK-induced HUVEC monolayer disruption. |
| Market | 6.5 billion US$ |
Indication
Cause
Incidence, Mortality
Symptoms
Unmet Needs
Mechanism of Action
Pathogenesis of HAE
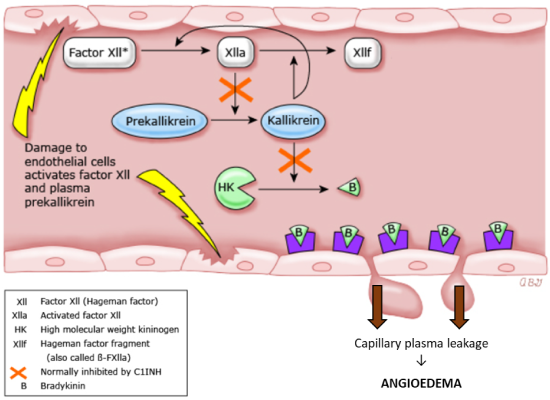
CU105 Principle of Action
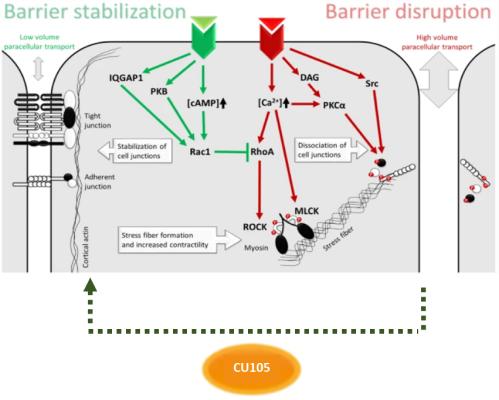
modified from N Engl J Med (2010)
Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol (2021)
Efficacy
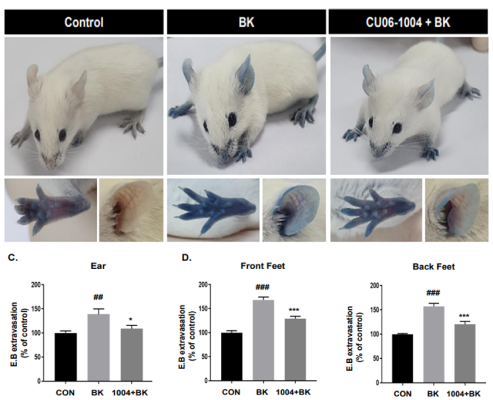
In vivo efficacy in BK (Bradykinin) model
Prevention of vascular hyperpermeability: measuring vascular leakage reduction with Evans Blue(dye)
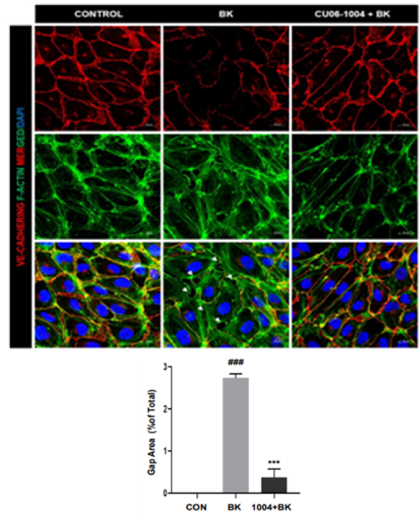
Inhibition of BK-induced HUVEC monolayer disruption
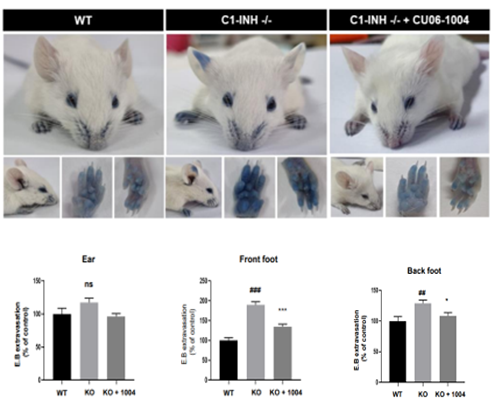
In vivo efficacy in C1-INH deficient model
Prevention of vascular hyperpermeability: measuring vascular leakage reduction with Evans Blue(dye)
Development
In vivo VE-cadherin immunofluorescence staining in BK model
Future Plan
In vivo FITC-dextran permeability assay in BK model
In vivo FITC-dextran permeability assay in BK model