파이프라인
파이프라인 상세
파이프라인
파이프라인 상세
CU102
급성폐손상(Acute Lung Injury) : CU06 적응증 확장 프로젝트
| 구분 | 내용 |
|---|---|
| CU102 | 급성폐손상(Acute Lung Injury) – CU06 확장 적응증 |
| Indication | 급성폐손상(Acute Lung Injury) |
| Unmet Needs | 글루코코르티코이드, 흡입성 산화질소, 활성단백C(APC)가 치료제로 시도되었으나 임상적 효능이 낮고, 부작용이 심합니다. |
| Mechanism of Action |
• 혈관내피세포의 항상성을 유지시키고 다양한 혈관 내피 활성제에 의해 유발되는 혈관 누출 및 염증을 억제합니다. |
| Efficacy & Safety |
• 급성 폐 손상을 위한 동급 최초의 혈관내피기능장애 차단제입니다. • 초기(급성) 단계에서 과도한 염증 반응을 억제합니다. • 중간(증식) 단계에서 폐포 상피 세포의 증식을 억제합니다. • 매개체(IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α)에 의해 파괴된 내피 장벽을 회복시킵니다. |
| Market |
• 2020년 1억57900만 달러/2030년 2억417만 달러(폐상해/CAGR: 4.2%) |
Indication
Cause
Incidence, Mortality
Symptoms
Unmet Needs
글루코코르티코이드, 흡입성 산화질소, 활성단백C(APC)가 치료제로 시도되었으나 임상적 효능이 낮고, 부작용이 심합니다.
Mechanism of Action
Pathogenesis of ALI
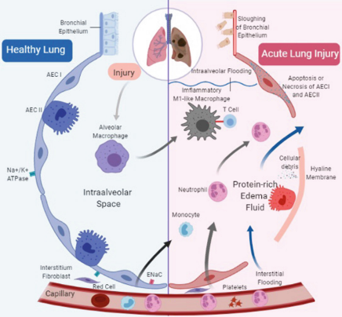
Damages on vascular endothelium and alveolar epithelium
Lung edema & Inflammation
Acute Lung Injury
Blocking blood vessel leakage and inflammation emerged as a treatment option
CU102: principle of action
Lungs in COVID-19 patients: vascular endothelial dysfunction observed as a key finding
CU102 blocks
The function of CU102 to inhibit endothelial cell-specific apoptosis, block blood vessel leakage and inflammation is noted as a novel treatment for ALI
▶ Proven excellent efficacy in ALI animal models
Efficacy
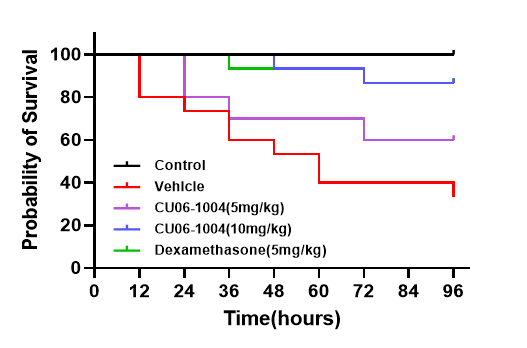
Improvement of survival rate & inhibition of pulmonary edema
Oral administration of CU102 (10 mpk) showed comparable survival rate to dexamethasone (steroid) and also relieved pulmonary edema
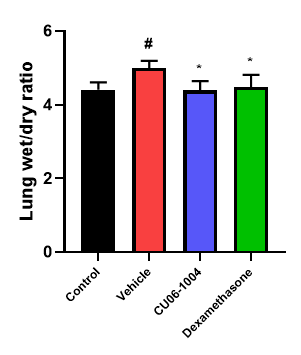
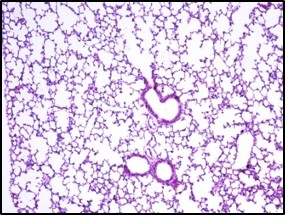
Inhibition of inflammation in lung tissue
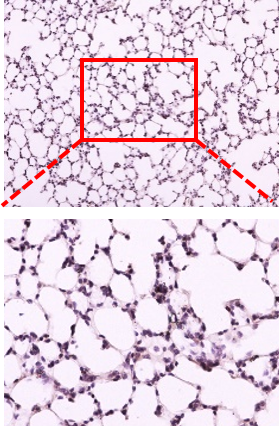
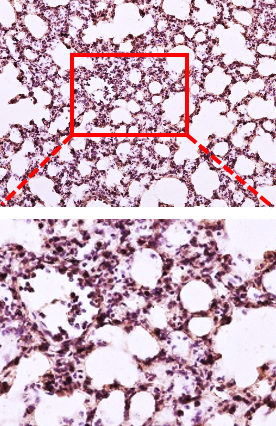
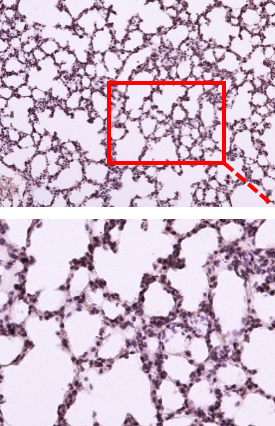
Reduces the influx of inflammatory cells into the lung tissue and tissue damage caused by LPS
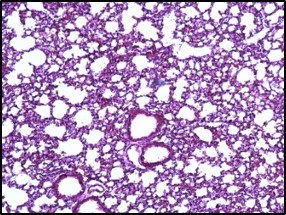
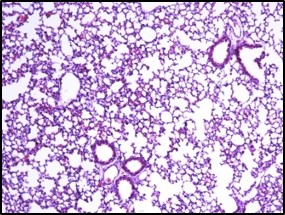
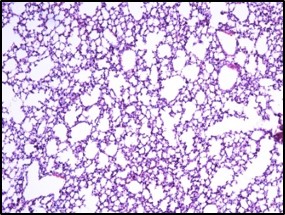
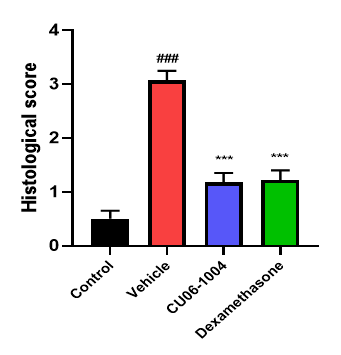
Electron microscope data of alveoli and pulmonary blood vessels
CU102 improves the alveolar-capillary barrier thickened by edema after LPS administration and significantly inhibits the adhesion of inflammatory cells to the inside of the pulmonary blood vessels
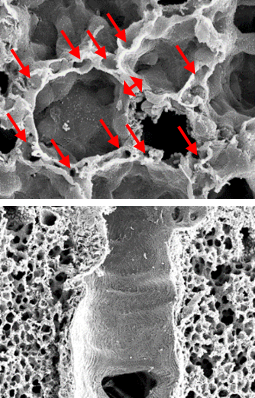
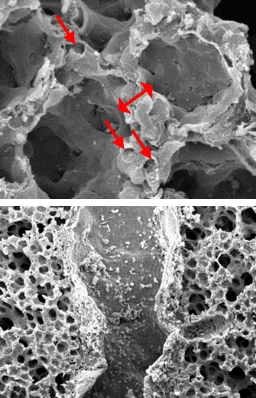
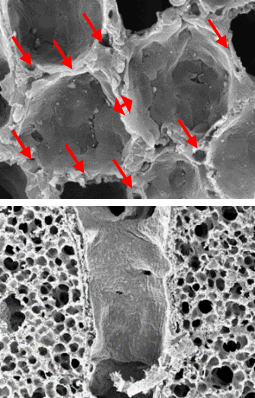
Arrow: normal capillary, Two-headed arrow: alveolar wall thickness
The structure of alveolar capillary endothelial cells damaged by LPS is improved
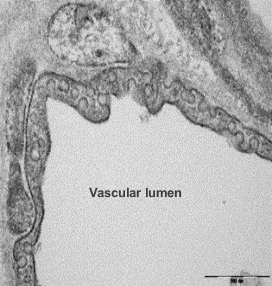
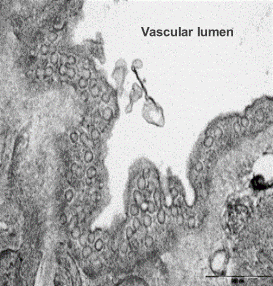
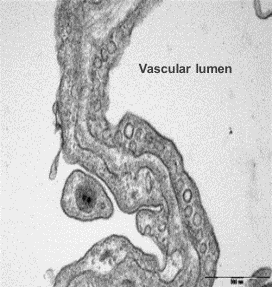
Additional Research
CU102 significantly inhibits MPO activity
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a peroxidase enzyme most abundantly expressed in neutrophil granulocytes
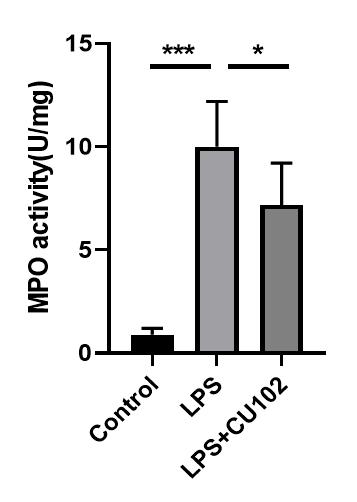
Cytokine Analysis in biological samples
BALF (Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid)
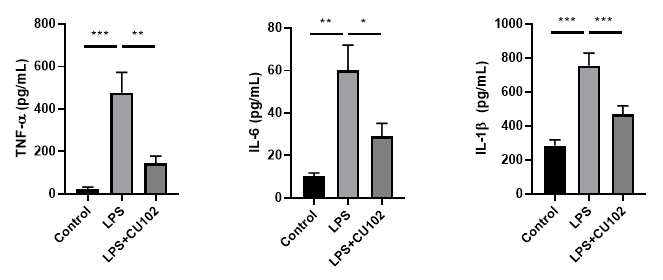
Serum
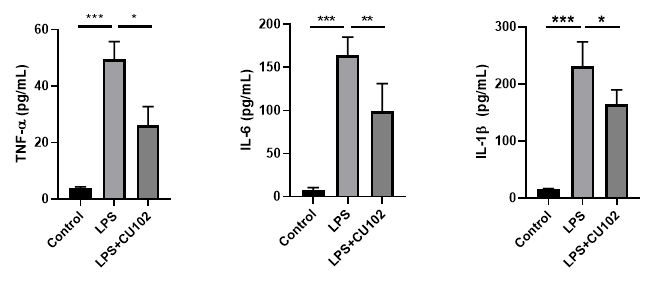
Additional Research
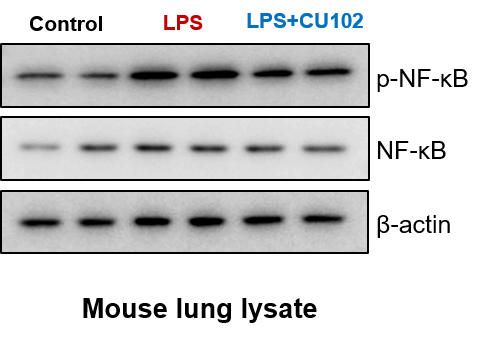
Immunohistology 및 western blot을 통한 CU102의 NF-ĸB 발현 및 활성화 억제 효과가 검증되었습니다.